POPULATION CONCEPTS
Population - a very important topic in Geography. The population of the world has continued to grow. In 1927 there were 2 billion people in the world. By 1987 the worlds population had reached 5 billion. Today the worlds population is 7 billion.
WORLD POPULATION
1. POPULATION DIVERSITY
Diversity and composition refer to HOW the population is made up – its like a snapshot of a country at a moment in time.
Comparing Auckland, Northland and West Coast - GENERAL POPULATION
Use this link to go to 'Quick Stats' on the Statistics NZ website. then click on the region.
Use this link to go to 'Quick Stats' on the Statistics NZ website. then click on the region.
- Find out the population of the area;
- What is the ranking of that region out of 16.
- What percentage of New Zealanders live there
ETHNICITY
SUMMARY of ethnicity in NZ
Use this link to go to the Statistics NZ site to see specific information about the different ethnicities in New Zealand. Click on 'view all chapters' to see specific information.
Comparing Auckland, Northland and West Coast - ETHNICITY
Use this link to go to 'Quick Stats' on the Statistics NZ website. then click on the region, and then click on 'view all sections' and then 'cultural diversity'. Complete the tasks set in class by your teacher
SUMMARY of ethnicity in NZ
Use this link to go to the Statistics NZ site to see specific information about the different ethnicities in New Zealand. Click on 'view all chapters' to see specific information.
Comparing Auckland, Northland and West Coast - ETHNICITY
Use this link to go to 'Quick Stats' on the Statistics NZ website. then click on the region, and then click on 'view all sections' and then 'cultural diversity'. Complete the tasks set in class by your teacher
AGE/SEX PYRAMIDS
Another important statistic is Age and Sex. This can be shown on an Age/Sex Pyramid.
|
Comparing Auckland, Northland and West Coast - AGE/SEX
Use this link to go to 'Quick Stats' on the Statistics NZ website. then click on the region, and then click on 'view all sections' and then 'age and sex'. Complete the tasks set in class by your teacher. | ||||||
2. POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
This is how and why population is spread across the landscape.
Key bits of info about the Distribution of New Zealand's Population:
WHERE do people live where they live? (read more here)
Key bits of info about the Distribution of New Zealand's Population:
- New Zealand’s population is unevenly distributed.
- NZ has a population density of 16 people per square kilometre
- 76% of New Zealanders live in the North Island
- 90% of New Zealanders live within 40km of the coast
- 87% of New Zealanders live in Urban Areas
- 31% of New Zealanders live in Auckland
WHERE do people live where they live? (read more here)
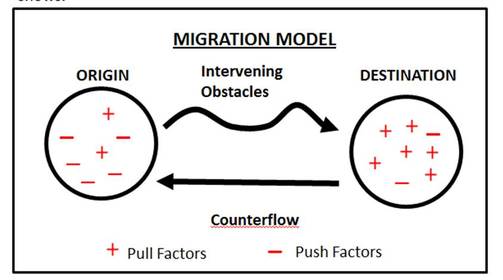
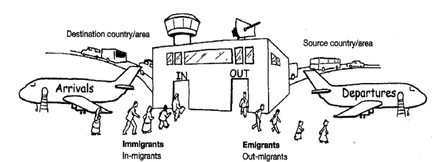
3. MIGRATION
|
There are 2 main types of migration - Internal (within New Zealand) and External (in and out of New Zealand).
Why do people move? •For a better job •To be closer to medical care •To go to university •To go to a better school •For a safer life •To be near/away from family •For a better quality of life •To avoid overcrowding •To live somewhere more affordable •To live somewhere with a better climate |
INTERNAL MIGRATION
1. Rural-Urban Drift
This is when people move from rural areas to urban areas. This is usually for jobs, better education, better medical services etc.
This is when people move from rural areas to urban areas. This is usually for jobs, better education, better medical services etc.
Many people move to Auckland from rural areas. Why do you think people move to Auckland? What does Auckland have that rural areas don't have?
3. Counterflow
This is movement of people back to smaller towns. y.
This is movement of people back to smaller towns. y.
EXTERNAL MIGRATION
|
|
|
|
1. Seasonal Migration
Due to the growth of Auckland and the Christchurch rebuild, New Zealand has had to advertise for construction workers overseas. Read more here. Read about Tongan Seasonal Workers here. Read about how New Zealand benefits from Temporary migration. From Immigration New Zealand - types of seasonal work visas. Video about Seasonal Workers |
|
2. Refugee Migration A refugee is a person who is outside their home country because they have suffered (or feared) persecution on account of race, religion, nationality, or political opinion; because they are a member of a persecuted social category of persons; or because they are fleeing a war. New Zealand has taken in refugees for many years. Use the Te Ara website to find out more. This information is what you read in class about refugee migration to New Zealand Videos about what its like to move to New Zealand. An opinion article in the NZ Herald from 30th August, 2015 'New Zealand needs to let in more refugees'. Video - The story of 700 Polish children (refugees from World War II) Video and article - Afghanistan refugees (example from class) |
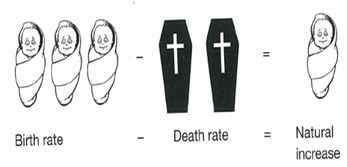
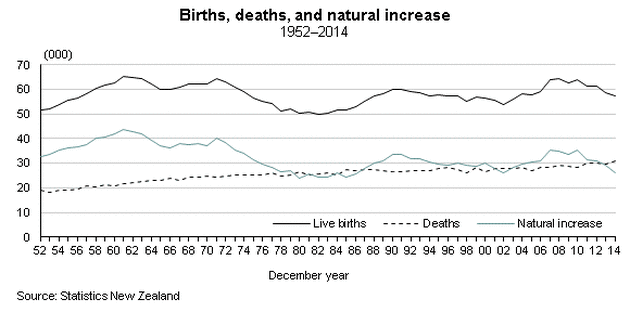
4. POPULATION CHANGE
Population is constantly changing over time.
CHANGE in New Zealand's population from the 1936 to what it might look like in 2068 - click here. OR try this link.
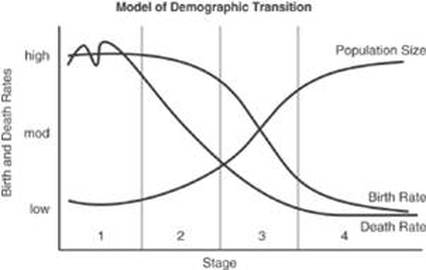
The Demographic Transition Model
What does the Demographic Transition Model show? Why have Birth Rates and Death Rates dropped?
5. POPULATION SUSTAINABILITY
Population Sustainability is the capacity of the environment to support a population in the longer term. Watch this video to see if the world can cope with 7 billion people - click here.
In class you looked at how New Zealand can sustain it's Aging Population.
Below is information about Auckland being able to sustain it's population as it continues to grow.
In class you looked at how New Zealand can sustain it's Aging Population.
Below is information about Auckland being able to sustain it's population as it continues to grow.