GLOBAL STUDY OF HIV/AIDS
Key Terms
Aspects of a geographic topic refer to a pattern in the topic, the causes of the pattern, and the effects of the topic on people’s lives in different parts of the world.
Geographic topic refers to a natural and/or cultural topic and/or study which has a global spatial dimension.
Global refers to regions or nations across different continents or hemispheres.
Spatial Pattern - A spatial arrangement on the earth’s surface. E.g. EVEN, UNEVEN, LINEAR, SPARSE, CLUSTERED , CONCENTRATED, DISPERSED, PERIPHERAL
Temporal Pattern - Time and how things changes over a period of time. E.g. EVEN, UNEVEN, FLUCTUATING, CYCLIC, REGULAR, IRREGULAR
HIV - Human Immuno-deficiency Virus. The HIV virus attacks the cells that fight disease, damaging the immune system. People who have the virus are know as HIV-Positive
AIDS - Aquired Immuno deficiency syndrome. A set of diseases that people get once their immune system is damaged by the HIV virus.
An NGO is a Non-Government Agency e.g. Oxfam
HIV prevalence is the percentage of the population living with HIV
Antiretroviral therapy is when people take medication to suppress the HIV virus and stop the progression of HIV disease.
An Epidemic is a wide spread disease, affecting more than one region or country
Sub-Saharan Africa refers to the countries in Africa that are south of the Sahara
Fluctuating means to vary irregularly.
Geographic topic refers to a natural and/or cultural topic and/or study which has a global spatial dimension.
Global refers to regions or nations across different continents or hemispheres.
Spatial Pattern - A spatial arrangement on the earth’s surface. E.g. EVEN, UNEVEN, LINEAR, SPARSE, CLUSTERED , CONCENTRATED, DISPERSED, PERIPHERAL
Temporal Pattern - Time and how things changes over a period of time. E.g. EVEN, UNEVEN, FLUCTUATING, CYCLIC, REGULAR, IRREGULAR
HIV - Human Immuno-deficiency Virus. The HIV virus attacks the cells that fight disease, damaging the immune system. People who have the virus are know as HIV-Positive
AIDS - Aquired Immuno deficiency syndrome. A set of diseases that people get once their immune system is damaged by the HIV virus.
An NGO is a Non-Government Agency e.g. Oxfam
HIV prevalence is the percentage of the population living with HIV
Antiretroviral therapy is when people take medication to suppress the HIV virus and stop the progression of HIV disease.
An Epidemic is a wide spread disease, affecting more than one region or country
Sub-Saharan Africa refers to the countries in Africa that are south of the Sahara
Fluctuating means to vary irregularly.
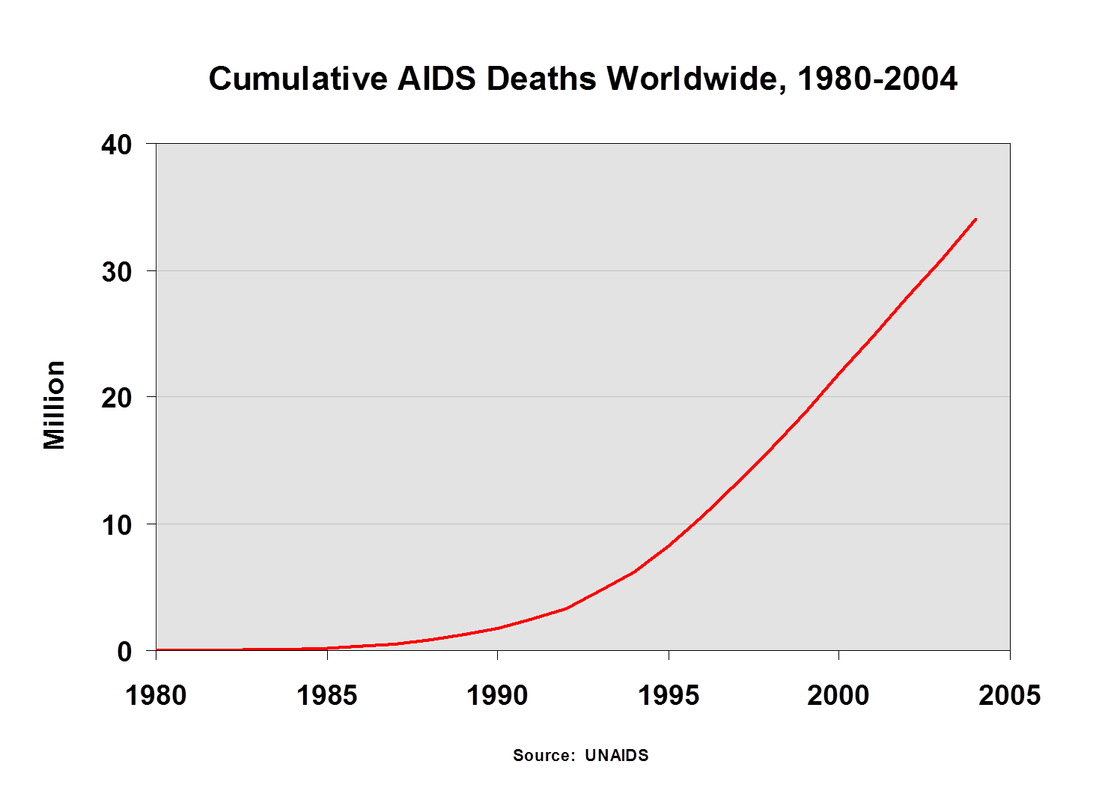
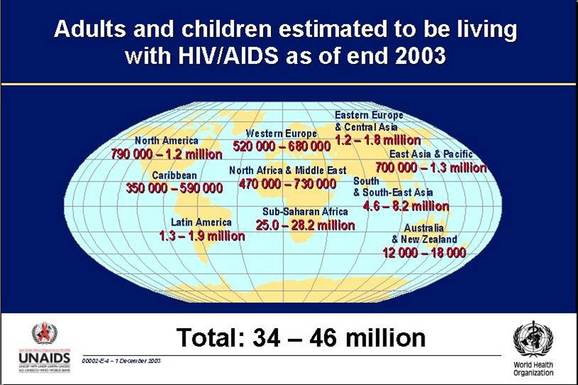
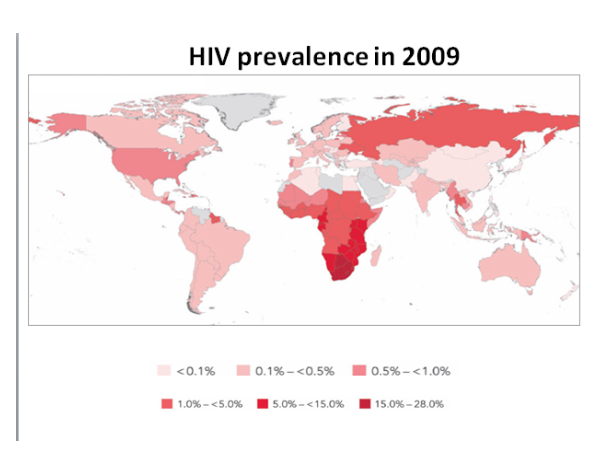
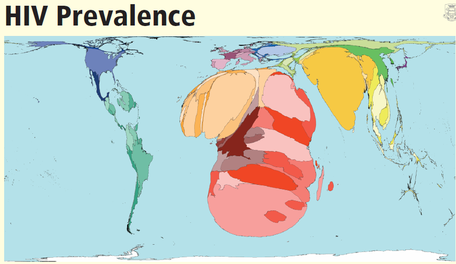
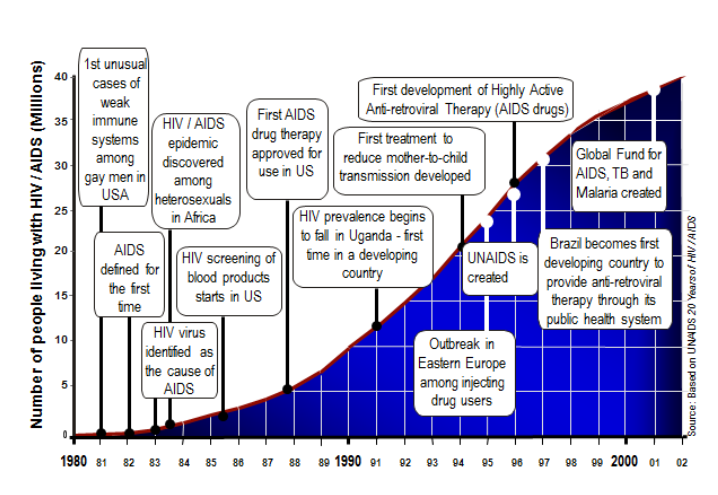
TEMPORAL PATTERNS of HIV/AIDS
These are the fact sheets you used in class to identify the TEMPORAL pattern of HIV/AIDS.
Write a summary for each of the regions explaining HOW the pattern of HIV infection and prevalence has CHANGED between 2001-2009.
Write a summary for each of the regions explaining HOW the pattern of HIV infection and prevalence has CHANGED between 2001-2009.
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
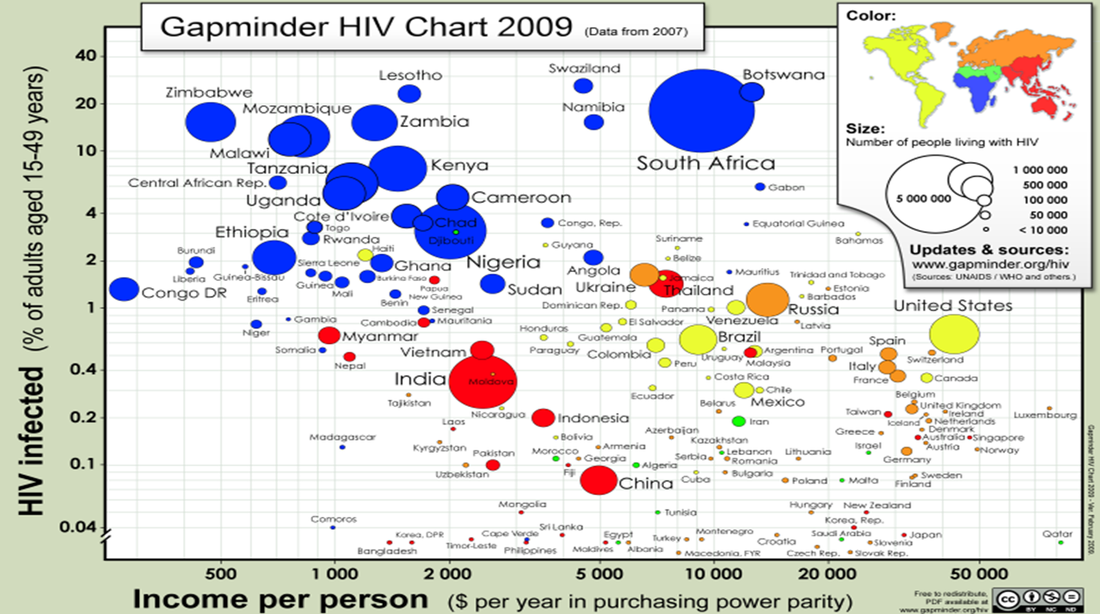
FACTORS/PROCESSES that produced the temporal pattern of HIV/AIDS
CLASS TASK: Use the following links to find out the reasons why HIV/AIDS is increasing or decreasing in 2 countries in each area of the world listed below (Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe). You could add to your annotated map with this information.
HIV/AIDS in Africa
HIV/AIDS in the Americas
HIV/AIDS in Asia and Europe
HIV/AIDS in Africa
HIV/AIDS in the Americas
HIV/AIDS in Asia and Europe
EXTRA INFORMATION: The videos below give you more information (to add to what you learnt in class) about the factors that have produced the temporal pattern of HIV/AIDS - how it is decreasing in some places and increasing in other places.
| uganda.docx | |
| File Size: | 34 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Significance to People's Lives
Use the following websites to find information on how the Global Study of HIV/AIDS is significant to people's lives:
The BBC website has a lot of useful information on HIV/AIDS.
This website has information specific to regions of the world.
Watch the video clips below.
The BBC website has a lot of useful information on HIV/AIDS.
This website has information specific to regions of the world.
Watch the video clips below.
|
|
|
ASSESSMENT
Below is the resource booklet you used in class. You will be given this resource in class but you can print your own copy and bring it to the assessment if you wish.
Assessment Dates
The assessment is in two parts. Part 1 will be completed in class time (your teacher will have these dates on the board in the classroom).
Part 2 is completed over a week at home (your teacher will have the due date for this on the board in the classroom)
The assessment is in two parts. Part 1 will be completed in class time (your teacher will have these dates on the board in the classroom).
Part 2 is completed over a week at home (your teacher will have the due date for this on the board in the classroom)
What you have to do for Achieved, Merit and Excellence:
ACHIEVED
Explain aspects of a geographic topic at a global scale involves:
Describing a spatial or temporal pattern of the geographic topic
Explaining the cause(s) that contribute to this pattern
Explaining the significance of the topic for people
MERIT
Explain, in depth, aspects of a geographic topic at a global scale involves:
Describing, in detail, a spatial or temporal pattern of the geographic topic using geographic terminology and concepts
Explaining, in detail, the cause(s) that contribute to this pattern
Explaining, in detail, the significance of the topic for people
EXCELLENCE
Explain, comprehensively, aspects of a geographic topic at a global scale involves:
Fully describing a spatial or temporal pattern of the geographic topic using geographic terminology and concepts
Fully explaining the cause(s) that contribute to this pattern
Fully explaining, showing insight, the significance of the topic for people